GitHub Actions and BitBucket Pipelines are amazing. You can control what is run using yaml files in your codebase.
You can run just about any command, and they provide a really powerful interface for browsing jobs and logs.
Many people are unaware, you can also control where your scripts are run. If you setup a tool called a Git Runner, you can run Git Actions anywhere, including from your local machine.
Enterprise Challenges
Implementing CI/CD in the enterprise has many challenges. When a site must be hosted and developed on private servers behind a firewall, you have a lot to think about:
-
How to install your own CI platform.
-
How to respond to events, like a webhook, polling, or a runner. Are you allowed to expose your CI server to the web?
-
How to launch (and destroy) new sites automatically on pull requests, matching production server config.
-
How to manage secrets securely.
-
How to manage system users and SSH access securely.
-
How to grant your server access to the code and live data securely via SSH.
-
How to control quality and manage releases successfully.
A New Way
With the right tools, you can leverage the powerful tools provided by GitOps platforms on your own servers, hosted anywhere using what are called runners.
A runner is a small script that runs on any server and listens for jobs from GitHub. Once connected, anything you push to your GitHub Workflow yaml files will run as that user on that server.
There are many benefits that might not seem obvious at first:
-
Run whatever CLI commands you want. Launch sites with docker-compose, DDEV, kubectl… whatever is in your Workflow.yml files is what happens.
-
Runs under the user of your choice. I typically setup a user called “platform” that has permission to run DDEV and has SSH access to clone code and environments.
-
Jobs run almost immediately. The Runner is sitting there waiting. The moment a job is queued, if it’s available, it starts running the scripts.
-
Jobs can be run on queue. Makes a great Drupal cron runner, because you can see every single one as a github action.
-
Jobs can be run on command. GitHub offers an interface to manually start a workflow.
-
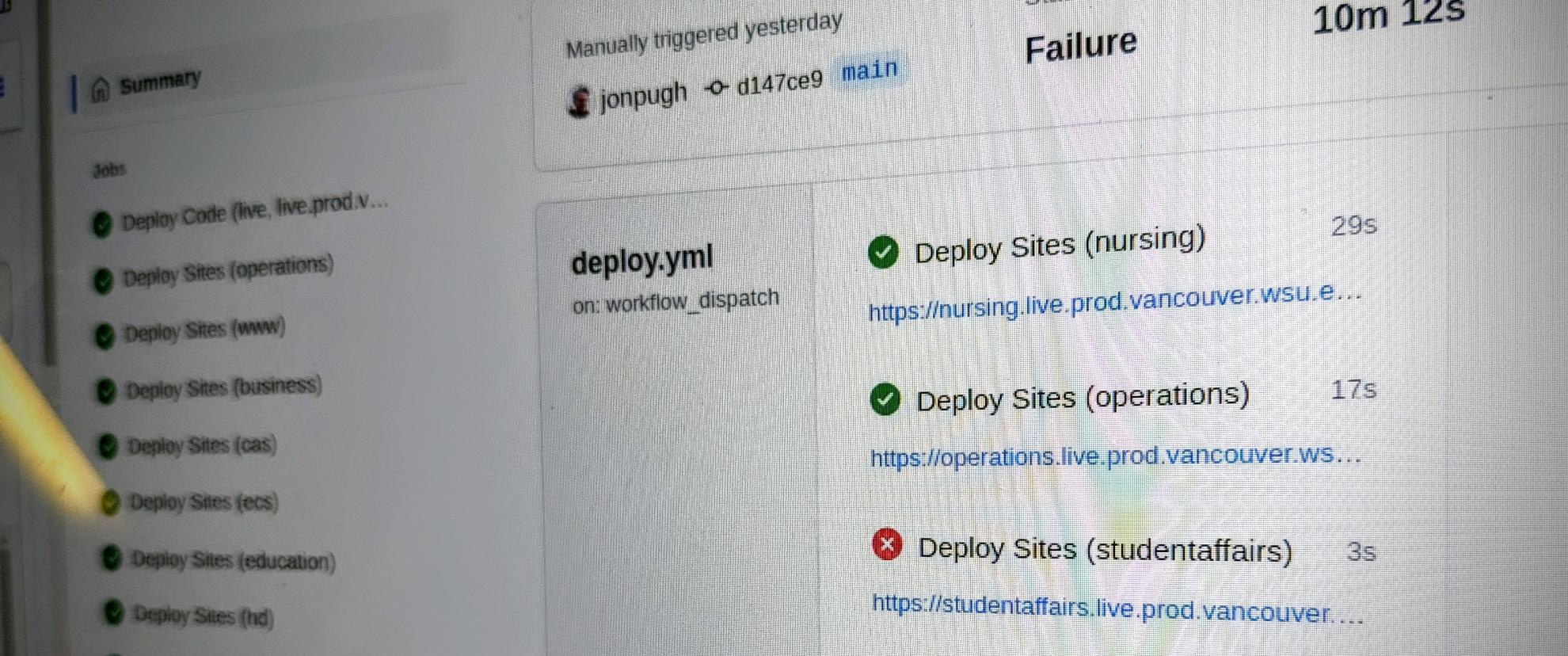
All jobs are logged in GitHub. This part is amazing. You can see all activity through the GitHub Actions tab.
-
Effortless GitHub API integration. Just having a Workflow file provides direct integration with GitHub’s Commit Status, Deployment, & Environments APIs. This is my favorite part. No GitHub API integration needed.
-
Secrets management. All GitHub Secrets are delivered to the runner. You don’t have to store them on the server at all. Anyone who has admin access can update the secrets and re-run the Deploy workflow to reset things that are needed, like SSH or API key updates.
-
The entire system can be accessed through the GitHub interface. There is no other dashboard needed. Test results, logs, artifacts, and links to preview sites are all available directly in the GitHub.com interface. And finally...
-
Your sites stay online and are accessible by your team! Unlike hosted CI environments, which are destroyed as soon as they finish running, Self-hosted runners can deploy fully running sites to your servers that can be accessed following the policies of your enterprise.
This new pattern has a lot of parts. I'll be writing more about it often. Check out this quick 10 minute video of me using the platform for this site: https://www.thinkdrop.net/deploying-new-feature-drupal-10-minutes-self-…
I’ve created a standard Ansible role for setting up a server to do this. I call it Operations Site Runner.
Check out more about the Operations Site Runner here.
If you ever want to talk about how you can get CI/CD going for your enterprise, get in touch!
